Shin Splint Syndrome
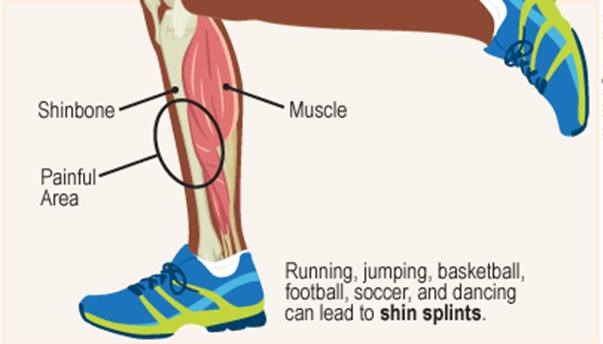
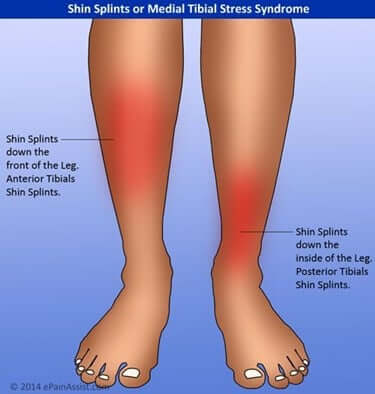
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS), is a term used to describe pain in the front of your lower leg and at times along the inside of the lower leg, next to the shin bone (tibia).
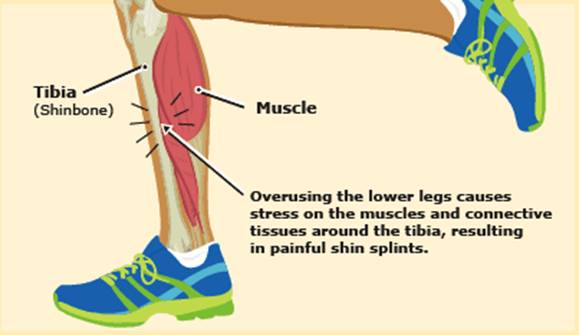
Shin splints is a cumulative stress disorder. Repeated pounding and stress on the bones, muscles, and joints of the lower legs causes pain & discomfort.
Shin splints frequently affect people who engage in moderate to heavy physical activities that involves running and jumping or stop-start sports such as tennis, racquetball, soccer, or basketball.
Causes –
The pain associated with shin splints results from excessive amounts of force on the shin bone and the tissues attaching the shin bone & this in turn causes the muscles to swell, increasing the pressure against the bone, leading to pain and inflammation.
The following mentioned are some known causes –
• Repetitive running on hard surfaces or forcible-excessive use of the foot flexors
• Lack of flexibility
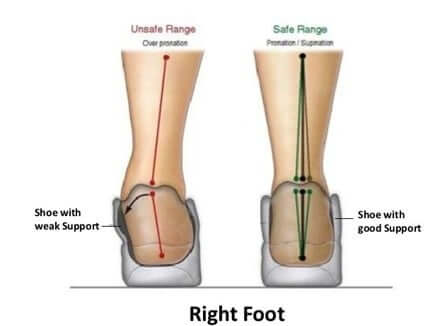
• Flat foot syndrome or high arches
• Improper training techniques
• Running on uneven terrain, such as hills, or hard surfaces, such as concrete
• Using inappropriate or worn-out shoes for running or workouts
• Participating in sports that have fast stops and starts (like soccer or tennis)
• Working out without warm-up or cool-down stretches
• Weak ankles, hips, or core muscles
• Suddenly increasing the duration, frequency or intensity of exercise
• Post stress fracture
Symptoms –
People with shin splints will experience some of the following symptoms:
• Dull ache in the front part of the lower leg
• Pain that develops during or after exercise
• Pain on either side of the shin bone
• Tenderness or soreness along the inner part of the lower leg
• Swelling in the lower leg (usually mild, if present)
Treatment –
• During initial phase of treatment, it is advised to change the training conditions like decreasing the running distance, intensity and frequency by 50% and avoid hills and uneven surfaces.
• Advised to continue low impact exercises like walking, swimming, biking or elliptical machine and after few weeks when pain subsides, may slowly increase training intensity and add sport-specific exercises.
• Icing helps to relieve pain and swelling, ice several times a day.
• Exercises to strengthen and stabilize your legs, ankles, hips and core will help prepare your legs to deal with high-impact sports.
• Proprioceptive balance training will increase the efficiency of the joints and postural-stabilizing muscles and help the body react to running surface incongruities.
• Stretch frequently your calf and hamstrings as tight muscles in leg causes more risk for shin splints. Make sure to warm up before exercise & stretch after exercise.
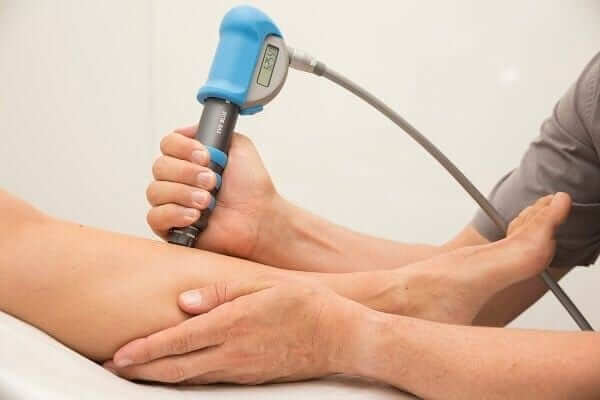
• Electrotherapeutic modalities like IFT, Therapeutic Ultrasound helps ease the soreness and tenderness.
• Shockwave therapy is an ideal treatment for chronic shin splints and shortens the healing time. Shockwave therapy combined with exercise program gives better results than the exercise program alone.
Prevent Shin Splints –
Here are some simple steps that you can take on your own:
1. Avoid sudden increase in physical activity. Lessen the impact.
2. DO NOT overdo your exercise routine. Go slower and increase your training slowly.
3. Exercise on softer surfaces when possible.
4. Consider shock-absorbing insoles. They might reduce shin splint symptoms and prevent recurrence.
5. Consider arch supports. Arch supports can help prevent the pain of shin splints, especially if you have flat arches.6. Stay at a healthy body weight.
Don’t delay your pain, get treated for your shin pain now! Reach out to us at-
Pooja Physiotherapy & Health Care Center Blk 77 Indus road #01-521S’160077. Call now @6384 5452 or Whatsapp @8322 3371 or Drop an email at info@physiopooja.com.sg